DEMAND
SUPPLY
PRICE
CHANGE
Economics. Perhaps not the first subject that you think about when starting or working in business. Economics is all about the big players and the academics, not for the smaller player surely? When it comes to the complex macro stuff of national budgets, hyper-inflation, and trade deficits but the basics apply to all businesses from the very big to the very smallest. Understanding the basics will help explain what you can and cannot do especially when it comes to the vital process of setting a price for you products, goods, and services.
List of Related Articles
The Basics of Economics
Economics is not about numbers but people and their behaviour in a market place. The numbers and graphs are there to show human behaviour and try to anticipate it. The purpose of economic is to try and model the future so that a business or government can work better towards its goals based on scarce resources. Scarce resources or “scarcity” is one of economic fundamentals. Let’s look at these fundamentals to set the foundations on an understanding of econmics.
Economics
The social science that studies the most efficient methods to use scarce resources.
Scarcity
Everything is limited by some factor. The factor can be something physical like space, mass, resistance etc or non-physical like time, attention, belief. This limitation creates scarcity of stuff or “resource”. Economics looks at the balance between humans wanting things within limited resources or ‘scarcity’.
Cost
Something you have to give up.
Opportunity Cost
Something you have given up due to making a decision. You could have had that something but the decision makes that impossible. Example would be using flour to make bread means there is no option to make a cake. The cake may have sold for more than the bread but there is less demand so may have not as the price was high whilst the bread was more likely to sell as the price was lower.
Production
Activity that produces something involving factors of production
Factors of Production
The things that are used to produce a product: land, labour (people), capital (money).
Making a Profit: Gross, Operating, Net
Setting Price: Fixed, Variable and Margin (and a few things inbetween)
Some helpful Economic Terms
Here are some common definitions to help with the clarity.
Consumer
A person or entity that uses the product that has been produced by a business.
Customer
A person or entity that purchases a product that has been produced by a business. A customer and a consumer can be the same person.
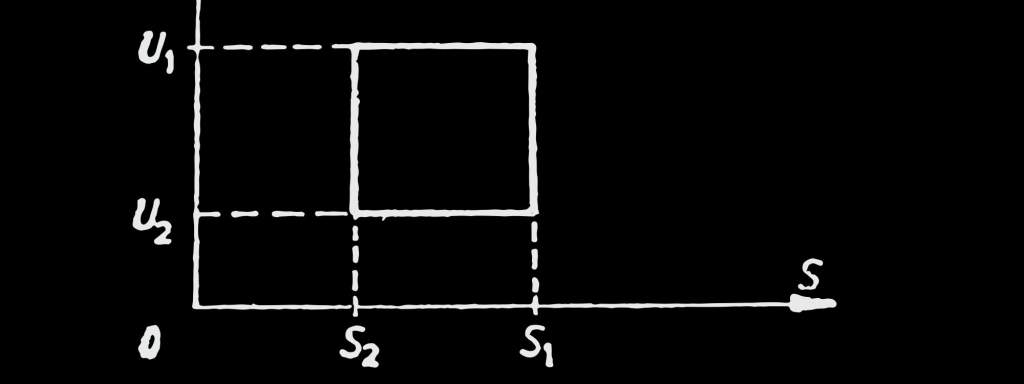
Demand
The market capacity for a product at a given time, price, and supply.
Entity
A non-person e.g. a business or service. An entity can purchase products (customer) and use products (consumer) on behalf of a person. The reason for the difference with a person is that some entities are legally accountable for actions i.e. a corporation.
Fixed Cost
A cost incurred in production that does not change with production volumes e.g. a machine, or a building.
Good
A physical product produced from physical resources. Physical resources are scares.
Person
A human being. Not a business or a service. People buy, sell and running businesses which can be entities.
Price
The monetary charge for a product. Normally in currency e.g. UK pounds Sterling or US Dollars.
Product
Something that satisfies a want on purchase and may fulfil a need when used. Note: a product is purchased. At the time of purchase the product is wanted or demanded.
Need
A motivation to fulfil a personal function. A need can be biological e.g. food, drink, air, material e.g. clothing, housing, or social e.g. friendship, entertainment, justice. If a need is not fulfilled then personal performance is effected.
Service
An activity completed by a person or entity on behalf of a person. A service is a type of product as it is produced.
Supply
The total supply of a product to a market based on market demand.
Variable Cost
A cost incurred in production that does change with production volumes e.g. materials, power, hours worked.
Want
A motivation by a person to have or experience something in the future. In business terms a want or demand is some thing a person will pay for to meet a need. A want can be fulfilled by a product.